Inverter Transformer Design Software
Inverter Transformer Design Software' title='Inverter Transformer Design Software' />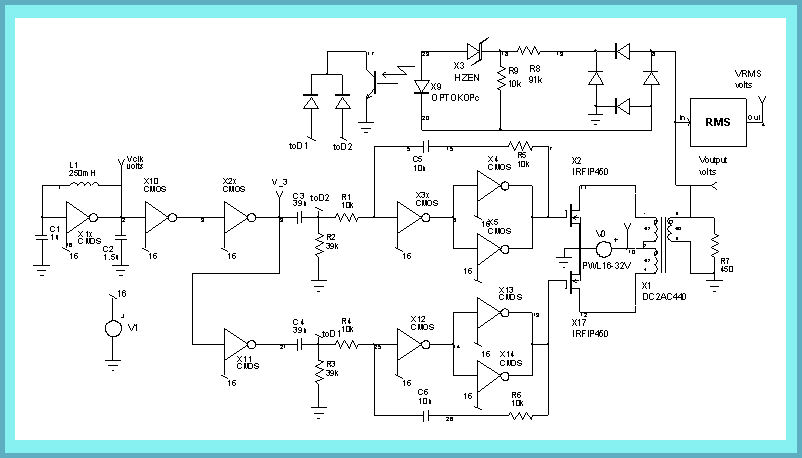 Transformer Ratings Csanyi. Group. Transformer Ratings. Transformer size or capacity is most often expressed in k. VA. We require 3. VA of power for this system is one example, or The facility has a 4. VAC feed rated for 1. VA. However, reliance upon only k. I want to step up the utility voltage 230Vrms by 12 and rectify it. I was thinking of using centre tapped transformer as a full wave rectifier. VA rating can result insafety and performance problems when sizing transformers to feed modern electronic equipment. Use of off the shelf, general purpose transformers for electronics loads can lead to power quality and siting problems Single phase electronic loads can cause excessive transformer heating. Electronic loads draw non linear currents, resulting in low voltage and output voltage distortion. Oversizing for impedance and thermal performance can result in a transformer with a significantly larger footprint. It is vital for the systems designer to understand all of the factors that affect transformer effectiveness and performance. Thermal Performance. Historically, transformers have been developed to supply 6. Hz, linear loads such as lights, motors, and heaters. Electronic loads were a small part of the total connected load. A system designer could be assured that if transformer voltage and current ratings were not exceeded, the transformer would not overheat, and would perform as expected. A standard transformer is designed and specified with three main parameters k. VA Rating, Impedance, and Temperature Rise. KVA Rating. The transformer voltage and current specification. KVA is simply the load voltage times the load current. A single phase transformer rated for 1. VAC and 2. 0 Amperes would be rated for 1. VA, or 2. 4 KVA thousand VA. Impedance. Transformer Impedance and Voltage Regulation are closely related a measure of the transformer voltage drop when supplying full load current. A transformer with a nominal output voltage of 1. VAC and a Voltage Regulation of 5 has an output voltage of 1. VAC at no load and 1. VAC 5 at full load the transformer output voltage will be 1. VAC at full load. Impedance is related to the transformer thermal performance because any voltage drop in the transformer is converted to heat in the windings. Temperature Rise. Steel selection, winding capacity, impedance, leakage current, overall steel and winding design contribute to total transformer heat loss. The transformer heat loss causes the transformer temperature to rise. Manufacturers design the transformer cooling, and select materials, to accommodate this temperature rise. Transformer Heat Loss. Use of less expensive material with a lower temperature rating will require the manufacturer to design the transformer for higher airflow and cooling, often resulting in a larger transformer. Power-eSim.png' alt='Inverter Transformer Design Software' title='Inverter Transformer Design Software' />National Electrical Code explanations, training and tips. Includes downloadable resources and a forum. Use of less expensive material with a lower temperature rating will require the manufacturer to design the transformer for higher airflow and cooling, often resulting. SN6501 ACTIVE LowNoise 350 mA, 410 kHz Transformer Driver for Isolated Power Supplies. How To Bypass LCD TV Inverter Board Shutdown Backlight System. Complaint Hisense TLM46V66PK LCD TV With Display Shutdown Problem in Few Seconds. Power inverter is a very useful device which can convert Low voltage from a DC source to high voltage AC. The most common power inverter is 12V to 240V inverter. Use of higher quality materials with a higher temperature rating permits a more compact transformer design. Transformer Insulation Systems. K Factor Transformer Rating. In the 1. 98. 0s, power quality engineers began encountering a new phenomenon non linear loads, such as computers and peripherals, began to exceed linear loads on some distribution panels. This resulted in large harmonic currents being drawn, causing excessive transformer heating due to eddy current losses, skin effect, and core flux density increases. Standard transformers, not designed for nonlinear harmonic currents were overheating and failing even though RMS currents were well within transformer ratings. In response to this problem, IEEE C5. A k factor was the result, calculated from the individual harmonic components and the effective heating such a harmonic would cause in a transformer. Transformer manufacturers began designing transformers that could supply harmonic currents, rated with a k factor. Typical K factor applications include K 4 Electric discharge lighting, UPS with input filtering, Programmable logic controllers and solid state controls. K 1. 3 Telecommunications equipment, UPS systems, multi wire receptacle circuits in schools, health care, and production areas. K 2. 0 Main frame computer loads, solid state motor drives, critical care areas of hospitalsK factor is a good way to assure that transformers will not overheat and fail. How To Setup Sql_Latin1_General_Cp1_Ci_As. However, K factor is primarily concerned with thermal issues. Selection of a K factor transformer may result in power quality improvement, but this depends upon manufacturer and design. Transformer Impedance. Transformer impedance is the best measure of the transformers ability to supply an electronic load with optimum power quality. Many power problems do not come from the utility but are internally generated from the current requirements of other loads. While a K factor transformer can feed these loads and not overheat, a low impedance transformer will provide the best quality power. As an example, consider a 5 impedance transformer. When an electronic load with a 2. A low impedance transformer 1 would provide only a 2 voltage sag a substantial improvement. Transformer impedance may be specified as a percentage, or alternately, in Ohms from Phase Phase or Phase Neutral. High Frequency Transformer Impedance. Most transformer impedance discussions involve the 6. Hz transformer impedance. This is the power frequency, and is the main concern for voltage drops, fault calculations, and power delivery. However, nonlinear loads draw current at higher harmonics. Voltage drops occur at both 6. Hz and higher frequencies. It is common to model transformer impedance as a resistor, often expressed in ohms. In fact, a transformer behaves more like a series resistor and inductor. The voltage drop of the resistive portion is independent of frequency, the voltage drop of the inductor is frequency dependent. Standard Transformer impedances rise rapidly with frequency. However, devices designed specifically for use with nonlinear loads use special winding and steel lamination designs to minimize impedance at both 6. Hz and higher frequencies. As a result, the output voltage of such designs is far better quality than for standard transformers. Recommendations for Transformer Sizing. System design engineers who must specify and apply transformers have several options when selecting transformers. Do It Yourself Approach. With this approach, a larger than required standard transformer is specified in order to supply harmonic currents and minimize voltage drop. Transformer oversizing was considered prudent design in the days before transformer manufacturers understood harmonic loads, and remains an attractive option from a pure cost standpoint. However, such a practice today has several problems A larger footprint and volume than low impedance devices specifically designed for non linear loads. Poor high frequency impedance. Future loads may lead to thermal and power quality problems. Standard Isolation Transformer. K factor Rated Transformers. Selecting and using K factor rated transformers is a prudent way to ensure that transformer overheating will not occur. Unfortunately, lack of standardization makes the K factor rating a measure only of thermal performance, not impedance or power quality. Percent Impedance. Some manufacturers achieve a good K factor using design techniques that lower impedance and enhance power quality, others simply derate components and temperature ratings. Only experience with a particular transformer manufacturer can determine if a K factor transformer addresses both thermal and power quality concerns. Transformers Designed for Non Linear Loads.
Transformer Ratings Csanyi. Group. Transformer Ratings. Transformer size or capacity is most often expressed in k. VA. We require 3. VA of power for this system is one example, or The facility has a 4. VAC feed rated for 1. VA. However, reliance upon only k. I want to step up the utility voltage 230Vrms by 12 and rectify it. I was thinking of using centre tapped transformer as a full wave rectifier. VA rating can result insafety and performance problems when sizing transformers to feed modern electronic equipment. Use of off the shelf, general purpose transformers for electronics loads can lead to power quality and siting problems Single phase electronic loads can cause excessive transformer heating. Electronic loads draw non linear currents, resulting in low voltage and output voltage distortion. Oversizing for impedance and thermal performance can result in a transformer with a significantly larger footprint. It is vital for the systems designer to understand all of the factors that affect transformer effectiveness and performance. Thermal Performance. Historically, transformers have been developed to supply 6. Hz, linear loads such as lights, motors, and heaters. Electronic loads were a small part of the total connected load. A system designer could be assured that if transformer voltage and current ratings were not exceeded, the transformer would not overheat, and would perform as expected. A standard transformer is designed and specified with three main parameters k. VA Rating, Impedance, and Temperature Rise. KVA Rating. The transformer voltage and current specification. KVA is simply the load voltage times the load current. A single phase transformer rated for 1. VAC and 2. 0 Amperes would be rated for 1. VA, or 2. 4 KVA thousand VA. Impedance. Transformer Impedance and Voltage Regulation are closely related a measure of the transformer voltage drop when supplying full load current. A transformer with a nominal output voltage of 1. VAC and a Voltage Regulation of 5 has an output voltage of 1. VAC at no load and 1. VAC 5 at full load the transformer output voltage will be 1. VAC at full load. Impedance is related to the transformer thermal performance because any voltage drop in the transformer is converted to heat in the windings. Temperature Rise. Steel selection, winding capacity, impedance, leakage current, overall steel and winding design contribute to total transformer heat loss. The transformer heat loss causes the transformer temperature to rise. Manufacturers design the transformer cooling, and select materials, to accommodate this temperature rise. Transformer Heat Loss. Use of less expensive material with a lower temperature rating will require the manufacturer to design the transformer for higher airflow and cooling, often resulting in a larger transformer. Power-eSim.png' alt='Inverter Transformer Design Software' title='Inverter Transformer Design Software' />National Electrical Code explanations, training and tips. Includes downloadable resources and a forum. Use of less expensive material with a lower temperature rating will require the manufacturer to design the transformer for higher airflow and cooling, often resulting. SN6501 ACTIVE LowNoise 350 mA, 410 kHz Transformer Driver for Isolated Power Supplies. How To Bypass LCD TV Inverter Board Shutdown Backlight System. Complaint Hisense TLM46V66PK LCD TV With Display Shutdown Problem in Few Seconds. Power inverter is a very useful device which can convert Low voltage from a DC source to high voltage AC. The most common power inverter is 12V to 240V inverter. Use of higher quality materials with a higher temperature rating permits a more compact transformer design. Transformer Insulation Systems. K Factor Transformer Rating. In the 1. 98. 0s, power quality engineers began encountering a new phenomenon non linear loads, such as computers and peripherals, began to exceed linear loads on some distribution panels. This resulted in large harmonic currents being drawn, causing excessive transformer heating due to eddy current losses, skin effect, and core flux density increases. Standard transformers, not designed for nonlinear harmonic currents were overheating and failing even though RMS currents were well within transformer ratings. In response to this problem, IEEE C5. A k factor was the result, calculated from the individual harmonic components and the effective heating such a harmonic would cause in a transformer. Transformer manufacturers began designing transformers that could supply harmonic currents, rated with a k factor. Typical K factor applications include K 4 Electric discharge lighting, UPS with input filtering, Programmable logic controllers and solid state controls. K 1. 3 Telecommunications equipment, UPS systems, multi wire receptacle circuits in schools, health care, and production areas. K 2. 0 Main frame computer loads, solid state motor drives, critical care areas of hospitalsK factor is a good way to assure that transformers will not overheat and fail. How To Setup Sql_Latin1_General_Cp1_Ci_As. However, K factor is primarily concerned with thermal issues. Selection of a K factor transformer may result in power quality improvement, but this depends upon manufacturer and design. Transformer Impedance. Transformer impedance is the best measure of the transformers ability to supply an electronic load with optimum power quality. Many power problems do not come from the utility but are internally generated from the current requirements of other loads. While a K factor transformer can feed these loads and not overheat, a low impedance transformer will provide the best quality power. As an example, consider a 5 impedance transformer. When an electronic load with a 2. A low impedance transformer 1 would provide only a 2 voltage sag a substantial improvement. Transformer impedance may be specified as a percentage, or alternately, in Ohms from Phase Phase or Phase Neutral. High Frequency Transformer Impedance. Most transformer impedance discussions involve the 6. Hz transformer impedance. This is the power frequency, and is the main concern for voltage drops, fault calculations, and power delivery. However, nonlinear loads draw current at higher harmonics. Voltage drops occur at both 6. Hz and higher frequencies. It is common to model transformer impedance as a resistor, often expressed in ohms. In fact, a transformer behaves more like a series resistor and inductor. The voltage drop of the resistive portion is independent of frequency, the voltage drop of the inductor is frequency dependent. Standard Transformer impedances rise rapidly with frequency. However, devices designed specifically for use with nonlinear loads use special winding and steel lamination designs to minimize impedance at both 6. Hz and higher frequencies. As a result, the output voltage of such designs is far better quality than for standard transformers. Recommendations for Transformer Sizing. System design engineers who must specify and apply transformers have several options when selecting transformers. Do It Yourself Approach. With this approach, a larger than required standard transformer is specified in order to supply harmonic currents and minimize voltage drop. Transformer oversizing was considered prudent design in the days before transformer manufacturers understood harmonic loads, and remains an attractive option from a pure cost standpoint. However, such a practice today has several problems A larger footprint and volume than low impedance devices specifically designed for non linear loads. Poor high frequency impedance. Future loads may lead to thermal and power quality problems. Standard Isolation Transformer. K factor Rated Transformers. Selecting and using K factor rated transformers is a prudent way to ensure that transformer overheating will not occur. Unfortunately, lack of standardization makes the K factor rating a measure only of thermal performance, not impedance or power quality. Percent Impedance. Some manufacturers achieve a good K factor using design techniques that lower impedance and enhance power quality, others simply derate components and temperature ratings. Only experience with a particular transformer manufacturer can determine if a K factor transformer addresses both thermal and power quality concerns. Transformers Designed for Non Linear Loads.
